| CAS
NO. |
55406-53-6 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
259-627-5 |
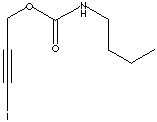
| FORMULA |
C8H12INO2NHCO2CH2CCl |
| MOL
WT. |
281.09 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
IPBC;
3-Iodo-2-propynyl N-butylcarbamate; Troysan;
|
| 3-Iodo-2-propynyl butylcarbamate; |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white
to off-white powder |
| MELTING POINT |
64
- 67 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.16 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
150
(mg/l) |
|
SOLUBILITY
|
PG (10), MEG (5), DEG (30), PEG (40), Alcohol (20) |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
FLASH
POINT
|
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under normal conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
Iodopropynyl Butylcarbamate is used as a broad spectrum biocide or preservative
to inhibit the growth of microorganisms. End applications include metal
working fluids, polymer emulsions, and pigment dispersions, cosmetics, household
products, paints, adhesives, cements and inks. Carbamic acid is a compound of chemical formula H2NCOOH. But it exists only in
the form of carbamate (its salt or ester), carbamide (amide) and carbamoyl (acyl
radical). Carbamates , with general formula -NH(CO)O-, have functional groups next to the carbonyl group.
Carbamate is formed when a carbon dioxide reacts with the amino group
the COO- group is a resonance structure. Carbamate structure
inhibits cholinesterase and many insecticides and
parasiticides contain carbamate fuctional group. Carbamate is a
poisonous ingredient in insecticide. Other common examples of poisonous
ingredients in insecticide include organophosphates and dichlorobenzenes. It is highly toxic to human
also. Heavy exposure to IT can cause carbamate poisoning. Natural carbamide
(urea) can be found in protein metabolism in urine. Carbamoyl is the radical
NH2CO-, also called carbamyl. It is a radical formed from an organic acid by removal of a hydroxyl group.
It is involved in the biosynthesis of the
pyrimidine ring. Carbamoyl compounds, such as salicylamides, are important for
the preparation of pharmaceutical products, pesticides, dyes, and biosynthesis researches. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
to off-white powder |
|
ASSAY
|
98.0%
min
|
|
MELTING POINT |
64
- 67 C |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: C, Risk Phrases: 34, Safety Phrases: 25/36/37/39/45 |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF DISINFECTANT |
Disinfectant is
an agent applied to inanimate objects to destroy, neutralize, or inhibit the
growth of disease-carrying microorganisms, (whereas antiseptics are applied
primarily to living things). Heat and radiation are also disinfectants. Common
ingredients of chemical disinfectant are:
- Mercuric
Chlorides
- Formaldehyde
- 8-Hydroxyquinoline
- Copper
Hydroxide
- Cresol
- Alcohols
(Ethyl Alcohol; Isopropyl Alcohol)
- Iodines /
Iodophors
- Chlorine
releasing compounds
- Gluteraldehyde
- Phenolics
- Quaternary
Ammonium Compounds
|
|
PRICE |
|

|
